It is important to understand the difference between a website and a web application. A website is any online digital presence. A web application is any online digital presence driven…

The difference between a website and a web application, it matters.
It is important to understand the difference between a website and a web application. A website is any online digital presence. A web application is any online digital presence driven by an online data source (CMS or other database). Ten years ago, roughly 10% of all websites were data driven web applications. Today, roughly 90% of all websites are data driven applications.
A general website is a basic marketing site that is updated directly through FTP, SFTP or another standard publishing format. A general website may have server side code such as ASP, PHP, .NET or Cold Fusion but will not be driven by a CMS or other DB application.
Mini-Site (marketing)
A mini-site is defined as 1-5 static HTML pages. These will serve a purpose to inform or incite a call to action. A mini-site could also serve as a method to collect information from a user. Short forms are pretty standard on mini-sites.
Marketing site
A basic marketing site can have any number of pages and perform various functions as needed. It could connect to simple REST APIs for data and also have forms.
Technology (page code)
The latest websites use HTML5 and CSS3. Legacy sites may use HTML, XHTML or below. The older the site technology, the more upkeep it will have. The number one reason for maintenance costs is cross browser compliance. Be very specific during requirements gathering, always leaning to the latest browsers. Certain larger clients on corporate networks will be bound to older browser requirements.
General Updates
Maintenance on general websites varies, depending on how its developed. Maintenance on existing sites is usually very time consuming. No matter what the request, be sure to verify current development schedules and level of effort.
Specifications (expectations)
Account has the obligation to work with BA’s to develop detailed specifications so that development can reach those expectations. Account should also consult the development team (solution management) to determine capabilities within the necessary time frame.
Whenever possible, determine what is the maximum possible expectation and leave yourself a buffer. This should provide a few advantages. It will give the development team some breathing room in case other issues arise. It will allow for the possibility for over delivering or getting ahead of the next phase. It will also help to counteract the common occurrence of development promising more than can be delivered.
QA
The most important part of the process is the verification of the completed work as it pertains to the documented specifications. Sacrificing quality for the sake of meeting a deliverable should be unacceptable.
WEB APPLICATIONS
In the most general sense, web applications are any HTML based application that is driven by a datasource. A web application will have both a front-end and a back-end component. Each type of application will have its own set of pros and cons. It is very important to understand each of these. Outlined here are our current capabilities and we will be adding to those capabilities as new ones come on line.
CMS Driven Website
Almost every website since 2009 has some form of CMS on the backend. We primarily focus on WordPress (PHP), Drupal (PHP) and customizing Sharepoint (.NET). You can also look at CMS integration as a basic component to any site going forward, except marketing mini-sites as noted in the general website section.
WordPress sites are easily themed and provide ease of maintenance. Content additions can be handled by client provided the sections are laid out logically and in a pre-defined replicated structure. If standard features are necessary and deadlines are tight, this is a really good way to get it up quick.
Drupal is a little more complex CMS to work with but has many advantages over WordPress. From a development standpoint, if you are a developer, Drupal is a very strong tool. You can build out additional functionality without too much trouble.
Facebook(FB) Application
More and more, clients are wanting a “Facebook App”. It is important to note that your application doesn’t actually have to be in a FB tab to be a FB application. It simply needs to connect to your FB account using a method called “Facebook Connect”. Then it needs to perform some function that requires you or your friends’ info. There are lots of considerations. Consider your privacy settings, the privacy settings of your “friends” and the privacy settings of your friends’ friends.
Facebook announced in December 2012 that more users login via mobile devices than web-based logins.
Facebook Graph API
The Graph API is the core of Facebook Platform, enabling developers to read from and write data into Facebook. The Graph API presents a simple, consistent view of the Facebook social graph, uniformly representing objects in the graph (e.g., people, photos, events, and pages) and the connections between them (e.g., friend relationships, shared content, and photo tags). Source: Wikipedia
Authentication
Facebook authentication enables developers’ applications to interact with the Graph API on behalf of Facebook users, and it provides a single-sign on mechanism across web, mobile, and desktop apps. Source: Wikipedia
Social plugins (LIKE, ACTIVITY, SHARE, ETC)
Social plugins – including the Like Button, Sharing, Recommendations, and Activity Feed – enable developers to provide social experiences to their users with just a few lines of HTML. All social plugins are extensions of Facebook and are specifically designed so no user data is shared with the sites on which they appear. Source: Wikipedia
Open Graph protocol
The Open Graph protocol enables developers to integrate their pages into the social graph. These pages gain the functionality of other graph objects including profile links and stream updates for connected users. While currently Google still attracts more traffic than any other website, Facebook is a close second. Even without a good internal search engine, Facebook already drives more traffic for some searches, specifically social searches, than Google itself. And in attempting to link Facebook with the rest of the web, the Open Graph is creating Facebook’s own extensive and highly interactive version of a search engine. Web pages are turned into Open Graph Objects by adding metadata. As an example, the following is the Open Graph protocol markup for ie Keyboard on Software Master Center: Source: Wikipedia
HTML5 Mobile Application
Over the last 3 years, the landscape of web development has changed dramatically. It may surprise you but that landscape changes exponentially ever 2-3 months. When thinking of web, understand that there are 4 current major browsers that we develop against.
All major browsers except IE force updating to the latest versions. IE is implemented in many corporate networks as the web standard for security and application control. Many larger networks, including the largest healthcare networks still use integrated deployment strategies to cut down on IT costs so they roll out browser updates in mass. This is the reason why many of our clients are still on IE8.
Internet Explorer’s growth seems to be slowing. Global vs US stats show different data. IE is still the global leader while market share is divided well in the US.
HTML5 is a new development standard meant to add features and promote cross browser functionality. When developing applications with HTML5, we have to be aware of using tags in code that aren’t supported in older browsers. In some instances, we can add some libraries that will degrade our code to be supported by older versions of browsers.
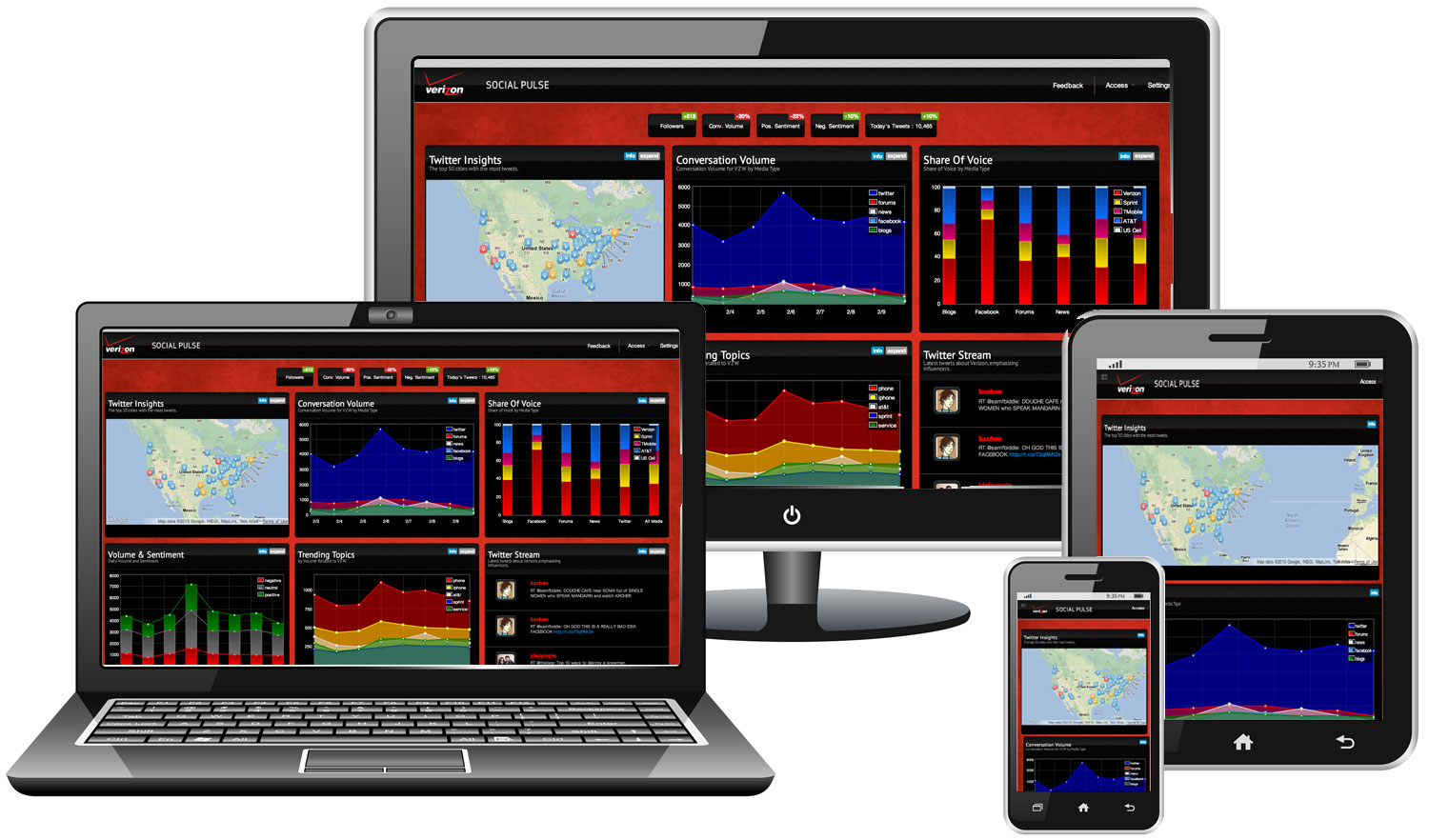
Custom Analytic Dashboard
Building dashboards has far reaching implications in how it relates to client relationships, WCG’s analytic reputation and how we handle the development. There are a number of considerations when building a dashboard. We are currently working on ways to give quick solutions for dashboard projects but the major considerations are budget, data sources, time and level of customization.
Dashboards must also go through a rigorous QA cycle for not only visuals but also data. Our reputation for analytics should be maintained appropriately. We currently have 2 developed frameworks that we can leverage to get clients up and running relatively quickly with the possibility to up sell a larger project (phased implementation).
When selling dashboards, analytic teams should be consulted to find out need before capability. We will create an online demo video that will outline dashboard capability for reference.
GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS
Responsive Development? Yes.
This isn’t even in question. It is a part of everything we do. The cost is negligible for any project to be responsive IF it is known up front. There is a difference between making an application work on smartphones and tablets and designing an experience tailor-made for those environments. That will reflect in level of effort. See my blog post on Responsive Development.
There aren’t any reasons why responsive development should not be done in every application you do. It is a consistent ask of every client (usually a week after launch). Clients should be aware that a large percent of today’s users only use mobile devices. In 2012, sales of tablets overtook the sales of desktop machines for the first time. The gap will only widen.
HTML Version
Generally speaking, all sites should be built to the latest code standard. HTML5 should be the base markup for all web applications. The development team should degrade the code (graceful degradation), that is, build the code so that lower browsers can view it within the limits of their capabilities.